Never going in with a Sicilian when death is on the line?
SolidGrue
I’m just this guy, you know?
- 0 Posts
- 54 Comments

 2·15 days ago
2·15 days agoTermux (on F-droid) is a userland environment that runs on top of your Android device’s kernel. It has Debian/Ubuntu-like package management system that pulls from repos maintained by the termux team. If the package is available for aarch64, its probably available in the termux repos. Its not so much of an app as it is an alternate userland that runs on top of the same kernel, but can interact with Android a couple of different ways.
The main Termux app gets you a basic command line environment with the usual tools included in a headless Linux install. From there you can select your preferred repos, do package updates, installs, etc, just like on a desktop or laptop. You could even install a desktop environment and use RDP to access it.
Then there are some companion apps that are useful:
- Termux:boot is like a primitive rc.d feature that executes upon boot up any scripts found in the termux ~/.termux/boot directory. You could use the feature to launch an SSH server, or perhaps start your syncthing service when the phone starts up.
- Termux:Tasker is a Tasker plugin that allows Tasker to launch scripts in .termux/tasker based on whatever triggers or profiles you define in Tasker. For example, stop or start selected services when connected to your home WiFi
- Termux:API is a set of termux utilities to interact with the Android API, and do things like send messages, interact with the camera or battery, and manipulate system settings.
So you could install the syncthing package in Termux and (after setting up Termux access for your internal storage) configure it to sync folders from your phone to wherever syncthing syncs. You’d set up a start script under Termux:boot to launch it when your phone starts, or Tasker to start/stop the service on your home WiFi.

 22·16 days ago
22·16 days agoFor the F-droid enabled users, it seems there’s a Syncthing app in the Termux repos:
~ $ apt show syncthing Package: syncthing Version: 1.28.0 Maintainer: @termux Installed-Size: 26.4 MB Homepage: https://syncthing.net/ Download-Size: 7857 kB APT-Sources: https://packages.termux.dev/apt/termux-main stable/main aarch64 Packages Description: Decentralized file synchronization
Probably all of them, at one time or another.

 20·1 month ago
20·1 month agoThere’s Gradle to crave joke to make here, but deploy keeps failing during dependency checks for humor.

 41·2 months ago
41·2 months agoNo worries, the other poster was just wasn’t being helpful. And/or doesn’t understand statistics & databases, but I don’t care to speculate on that or to waste more of my time on them.
The setting above maxes out at 24h in stock builds, but can be extended beyond that if you are willing to recompile the FTL database with different parameters to allow for a deeper look back window for your query log. Even at that point, a second database setting farther down that page sets the max age of all query logs to 1y, so at best you’d get a running tally of up to a year. This would probably at the expense of performance for dashboard page loads since the number is probably computed at page load. The live DB call is intended for relatively short windows vs database lifetime.
If you want an all-time count, you’ll have to track it off box because FTL doesn’t provide an all-time metric, or deep enough data persistence. I was just offering up a methodology that could be an interesting and beneficial project for others with similar needs.
Hey, this was fun. See you around.

 161·2 months ago
161·2 months agoRemoved by mod

 141·2 months ago
141·2 months ago#### MAXLOGAGE=24.0 Up to how many hours of queries should be imported from the database and logs? Values greater than the hard-coded maximum of 24h need a locally compiled `FTL` with a changed compile-time value.I assume this is the setting you are suggesting can extend the query count period. It still will only give you the last N hours’ worth of queries, which is not what OP asked. I gather OP wants to see the cumulative total of blocked queries over all time, and I doubt the FTL database tracks the data in a usable way to arrive at that number.

 192·2 months ago
192·2 months agoAh, well if you know differently then please do share with the rest of us? I think the phrasing in my post makes it pretty clear I was open to being corrected.

 162·2 months ago
162·2 months agoSo, like a running sum? No, I don’t think so, not in Pi-hole at least.
Pi-hole does have an API you could scrape, though. A Prometheus stack could track it and present a dashboard that shows the summation you want. There are other stats you could pull as well. This is a quick sample of what my home assistant integration sees
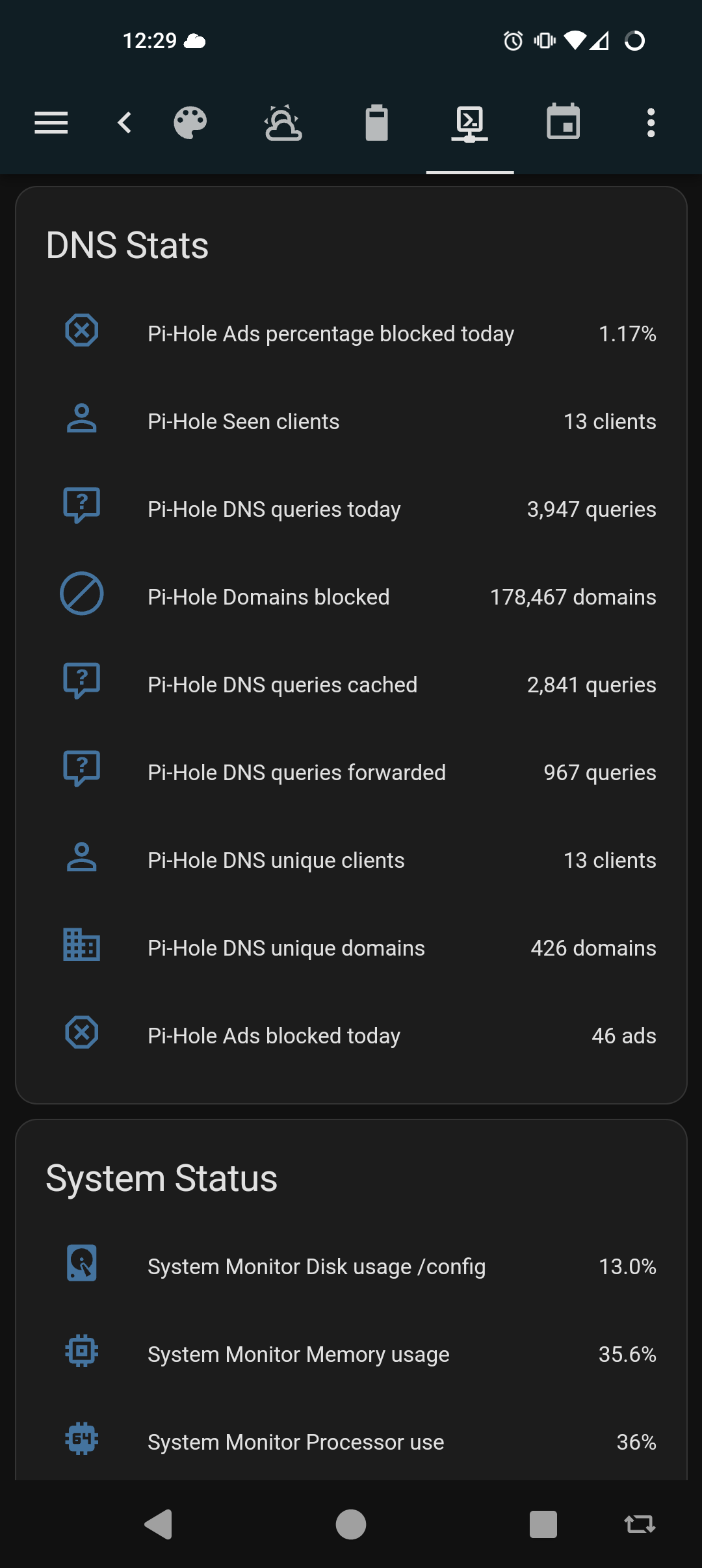

 371·2 months ago
371·2 months agoThat counter, I believe, for the last 24 hours. It will fluctuate up and down across your active daily periods

 54·2 months ago
54·2 months agoUnless I misunderstand your question, draw.io can be downloaded as a standalone Linux application and run locally.
Likewise, the Xfig package should he available in most Linux repos. It’s old, but good enough for a quick sketch.
edit: aha. My mistake. My eyes slid over ‘open source’ in the title*, and even still I hadn’t realized it was an Apache license.
* Whaaat, it was pre-coffee? Let the purest among us cast the first stone.
Looks like Python, but in an editor with a weird TUI scrollbar
Unbound will take updates via API. You could either write exit hooks on your clients, or use the “on commit” event on isc-dhcp-server to construct parameters and execute a script when a new lease is handed out.
I used to selfhost more, but honestly it started to feel like a job, and it was getting exhausting (maybe also irritating) to keep up with patches & updates across all of my services. I made decisions about risks to compromise and data loss from breaches and system failures. In the end, In decided my time was more valuable so now I pay someone to incur those risks for me.
For my outward facing stuff, I used to selfhost my own DNS domains, email + IMAP, web services, and an XMPP service for friends and family. Most of that I’ve moved off to paid private hosting. Now I maintain my DNS through Porkbun, email through MXroute, and we use Signal instead of XMPP. I still host and manage my own websites but am considering moving to a ghost.org account, or perhaps just host my blogs on a droplet at DO. My needs are modest and it’s all just personal stuff. I learned what I wanted, and I’m content to be someone else’s customer now.
At home, I still maintain my custom router/firewall services, Unifi wireless controller, Pihole + unbound recursive resolver, Wireguard, Jellyfin, homeassistant, Frigate NVR, and a couple of ADS-B feeders. Since it’s all on my home LAN and for my and my wife’s personal use, I can afford to let things be down a day or two til I get around to fixing it.
Still need to do better on my backup strategies, but it’s getting there.

 4·4 months ago
4·4 months agoI use Porkbuns API. It’s not sophisticated, but it works.

 8·4 months ago
8·4 months agoGandi changed their TOS and price structure last year, so I ported everything over to Porkbun for a small savings, but mostly as a big middle finger to Gandi.
If you’re gonna get banged that kind of cash for functions you’re already using, you may as well look at better registrars, and get better value for your spend.
Shop around.
You could source a pair of gigabit media converters and a length of fiber on Amazon for about $100. Just use the media converters to extend the Ethernet port from where the Internet hands off in your house over to your office. You can affix the fiber along baseboards and up over door frames with adhesive cleats and zip ties, or those nylon staples on a nail they use to tack down coax cable.
If you’re willing to spend a little more on the fiber for a custom color, you can probably even order the fiber in a more neutral color than SMF yellow to blend into the trim better.
If you just want each physical interface on your server to participate in a single VLAN, set the corresponding switch port as an access port in the desired VLAN, and then configure each server interface as a normal untagged interface.
You would only do tagged frames (802.1q trunking) if you wanted to support several VLANs on the switch port.


Thanks! I hate this. 🖤